Town population size and structuring into villages and households drive infectious disease risks in pre-healthcare Finland
Tarmo Ketola, Michael Briga, Terhi Honkola and Virpi Lummaa 2021: Proc R Soc B
DOI: 10.1098/rspb.2021.0356
ABSTRACT
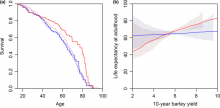
Social life is often considered to cost in terms of increased parasite or pathogen risk. However, evidence for this in the wild remains equivocal, possibly because populations and social groups are often structured, which affects the local transmission and extinction of diseases. We test how the structuring of towns into villages and households influenced the risk of dying from three easily diagnosable infectious diseases—smallpox, pertussis and measles— using a novel dataset covering almost all of Finland in the pre-healthcare era (1800–1850). Consistent with previous results, the risk of dying from all three diseases increased with the local population size. However, the division of towns into a larger number of villages decreased the risk of dying from smallpox and to some extent of pertussis but it slightly increased the risk for measles. Dividing towns into a larger number of households increased the length of the epidemic for all three diseases and led to the expected slower spread of the infection. However, this could be seen only when local population sizes were small. Our results indicate that the effect
of population structure on epidemics, disease or parasite risk varies between pathogens and population sizes, hence lowering the ability to generalize the consequences of epidemics in spatially structured populations, and mapping the costs of social life, via parasites and diseases.